Become a leader in the IoT community!
New DevHeads get a 320-point leaderboard boost when joining the DevHeads IoT Integration Community. In addition to learning and advising, active community leaders are rewarded with community recognition and free tech stuff. Start your Legendary Collaboration now!




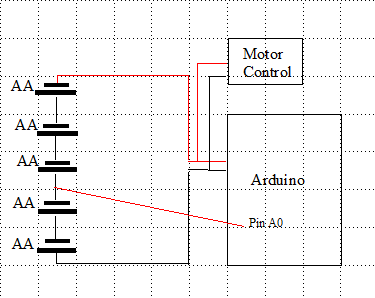



A voltage divider can work well, send the total voltage through a voltage divider, use R1 = 5.1k and R2 = 1k. If current consumption is a concern, you can use 51k and 10k. Then you can read the entire voltage of the battery. Then for the readings you are getting, is the distance between the battery and the A0 pin much? long distance affects readings. Also try and put a 100nf capacitor on the A0 pin to ground.
Thanks for the suggestion! The distance between the battery and A0 pin is about 7 – 10 cm does it effect the readings? , I’ll also add the 100nF capacitor to the A0 pin and see if that stabilizes the readings.”
Hello. @mr.aymen_ammari is tapping the voltage for two batteries => 1.5 x 2 =3 volts.
I’m confused why is a divider needed? Please correct me if im wrong, @afuevu_
Also @mr.aymen_ammari you can tap the entire 1.5 x 5 =7.5 volts directly by using voltage divider like @afuevu_ suggested. You can use any voltage divider calculator online for this purpose.
Distance affects readings, try and shorten the distance as much as possible.
Hello @bruce_wayne5006, a voltage divider is unnecessary if the total voltage is not more than 5v. But if the voltage is more than 5v, it is necessary.
That’s right! What he can actually do is tap the cumulative voltage of 7.5V using a divider. Maybe that is better than tapping only into part of the battery.
CONTRIBUTE TO THIS THREAD